Building on a track-record in covalent drug discovery1 (The Future of Covalent Drugs, Discovery Report Q3, C&EN, 2022), the EDV group aims at integrating the advantages of small molecule covalent ligands to advance novel applications in Chemical Biology and Drug Discovery. We are interested in developing novel assays and techniques to discover and optimize small molecule covalent binders for challenging targets, which have potential applications in the rising field of chemically induced proximity. Furthermore, we are constantly on the look for Chemical Biology methodologies that will enable understanding of small molecule and protein function in cells with a translational perspective.
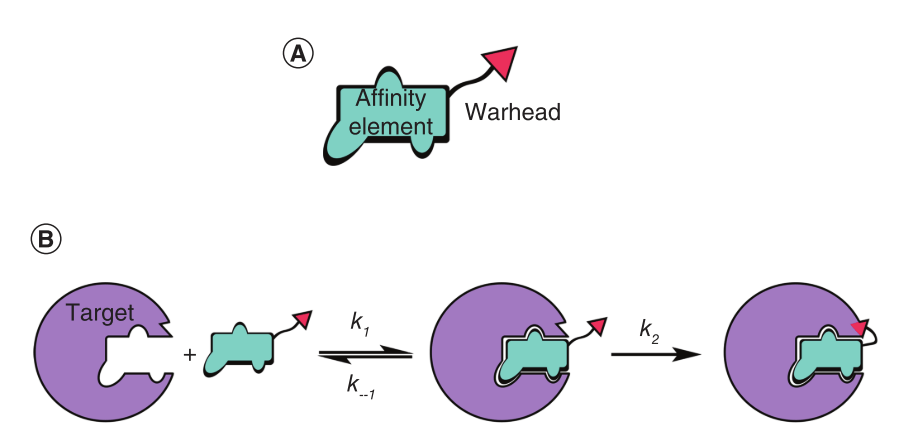
Current research lines are focused on PHOSphorylation TArgeting Chimeras (PHOSTACs), a chemically induced proximity approach2 that employs bifunctional ligands to recruit a protein phosphatase (PP) in the proximity of a phosphorylated protein of interest to drive targeted protein dephosphorylation.3 Small molecule PHOSTACs will be developed to uncover the role of the unknown phosphoproteome, which still represents the majority of all known phosphosites profiled in humans to date. Mainly focusing on cancer research, we aim to further study the mechanism of action of PHOSTACs and develop ligands with improved pharmacological properties to explore novel therapeutic opportunities in cancer, where protein hyperphosphorylation is a well-known driver of disease.
- De Vita E. (2020) 10 years into the resurgence of covalent drugs. Future Medicinal Chemistry, 13(2), 193-210. ↩︎
- Maneiro, M., De Vita, E., Conole, D., Kounde, C. S., Zhang, Q., & Tate, E. W. (2021). PROTACs, molecular glues and bifunctionals from bench to bedside: Unlocking the clinical potential of catalytic drugs. In Progress in Medicinal Chemistry (1st ed.). Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmch.2021.01.002 ↩︎
- Yamazoe, S., Tom, J., Fu, Y., Wu, W., Zeng, L., Sun, C., Liu, Q., Lin, J., Lin, K., Fairbrother, W. J., & Staben, S. T. (2020). Heterobifunctional Molecules Induce Dephosphorylation of Kinases-A Proof of Concept Study. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 63(6), 2807–2813. ↩︎
